- Start Framework Manager
and click on “Create new project”
- On clicking the link we
are asked to enter a name for the project. Enter a relevant name and location
for the project and then click on OK.
In this case we name our model as GOSALESDW.
- Now you are prompted to
select language for the project. In this case we select English as shown
in below screen shot and click on OK.
- Now you are prompted to
select the metadata source. Select Data
Sources (highlighted in screenshot) and click next. You can use any other type of datasource as present in the
list below depending on the project requirement.
5. On selecting
Datasources, a list of available data sources is populated. Select appropriate
datasource and click next.
Alternatively you can click on new
to create a new datasource. We already have a data source called DS_GOSALES, we
will use this here.
6. In the next screen you can
select the tables you want to Import in the Model. Alternatively you can
select Views,functions, procedures, Synonyms as per the project
requirement. Here we expand tables.
Select the required tables by clicking the check box and click Next.
7. In the next screen is the generate relationships screen.
You can click on the check box button for “Use primary and foreign keys” to
generate relationships. In this case we don’t want the relationships. Click on
the Import button. Ideally we avoid
pulling up existing relationships.
Click finish to
complete the import process.
8. Now you can see the Sample Project
in the project viewer pane of FM as shown below.
9. Rename the Datasource as “GOSALESDW_TRAINING” . The Model looks
like as shown below.
Right click on GOSALESDW_TRAINING to create a new namespace as shown in
screenshot below. Name it as DataBaseView.
Select all the tables in GOSALESDW_TRAINING
Namespace
Drop them into DataBaseView namespace. Now the model
looks like as shown below. All the tables are in DatabaseView. The Data base
view is designed such that it is exact replica of the Database tables. We do
not make any changes in table properties in this view. The next step is to
create a businessview.
10. Right Click on the GOSALESDW_TAINING
click CreateàNamespace.
Rename the namespace as “Business View” as
shown in the screen shot below. BusonessView is the Layer in which we alter
properties of tables and make required changes. There are four important thing
that we do in business Layer
a. Business Naming of Tables.
b. Set usage properties of
columns for all the tables
c. Create relationships among
tables
d. create calculations and
filters if any required at the FM level.
BusinessView is highlighted in
below screenshot. In businessView we can created query subjects of three types
a.
Model Query Subject
b.
Database Query Subject
c.
Stored procedure Query Subject
In this case we will create Model
Query Subject as we will pull queries from Database View.
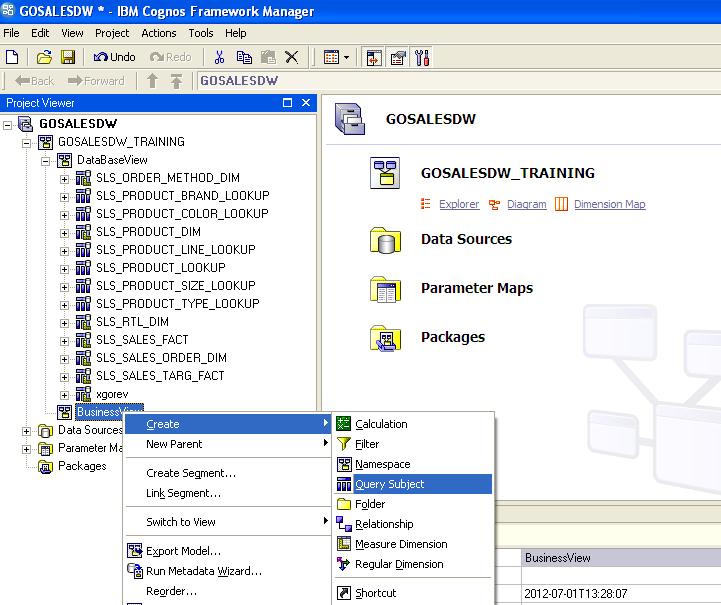
11. Right Click on the Business
view click CreateàQuery
Subject. (we will create Model query Item for the Business View).
12. You are asked for the type of the query Item you want to
create. We can create three types of query subjects
a. Data source query Subject
b. Model Query subject
c. Stored procedure query subject.
Create Model Query subject for the tables which are required
in the Business view from the database view.
Give a proper name to each query subject created in the
Business view.
In this case we have selected Model Query and named the
Query Item as D_ORDER_METHOD.
Click OK.
13. Drag the required columns from the Table in Database
view to the new Modal query Item. In this case we pull all the columns from the
D_CALENDAR table of the database view. Click OK. Similarly you can create Model query items for other required
Tables.
In the same manner pull all other relevant tables Model
query subject in the Businesslayer.
14. After pulling the required
tables in Business view. Expand each table and check the usage properties for
the columns.
There are three types of usage
properties
a. Identifier
b. Attribute
c. Fact
Make sure that usage property for
all the keys and date fields is set to Identifier. Usage should be set to Fact
for all numeric values and for the remaining items the property should be set
to attribute.
15. We need to create relationship
between the query items. To create a relationship Right Click on the query Item
Click Create àRelationship
as shown in the screenshot below.
16. A relationship definition
window as shown below opens up. You can define the relationship between the
fact and dimension table in this window. Make sure the cardinality is 1..n at
the Fact table end and is 1..1 at the dimension table side. After adding
appropriate link click on OK Same is shown in the below screen shot. The two
red arrows show cardinality between dimension and fact tables.
17. Next step is to create Report
View from business view. To do so we initially create Alias shortcuts for the
query items in the Business view and then drag them in to a new namespace
called Report view.
Now we have the alias shortcut of
the query Items present in the Business view in the Report View.
To create an alias shortcut right
click on the query item click Createàalias short cut. For Report View we can create star schema grouping of required dimensions and fact. In business View select required dimensions and fact, right click and select "Create Star Schema Grouping". Create a new Namespace whcih can be renamed to reporting view or can be given a relevant name.
18. The next step is to create a package from the Model. To create a new
package right click on Package folder present in the Project Viewer pane of FM and click CreateàPackage.
Process to create package is
shown in below screenshot.
19. Next window asks for providing a name to package. Enter
appropriate name and click next. You can write a small description if you wish
to.
20. Next window asks for the object definitions to be
included in the package.
Select the desired objects and click next. In this case we select
BusinessView.
21. Next window asks you for the “select function list” wherein you can select
functions that you want to be there in “available
functions list” the model while creating reports. In this case we keep only
SQL server. However, you can select all functions. The window for the same is
shown in below screen shot. After selection appropriate functions click Finish.
22. Finally after clicking on
Finish you get following message. You can click Yes to publish the package immediately or click on No to publish package at later point of
time.
If you wish to set “Governers” click no . Select Package click ProjectàEdit
Governers. Following window appears wherein you can set the governors like
Query execution time limit, cross product (allow/deny) etc for the selected
package.
23. On clicking YES a
new window as shown in screen shot below appears which asks for the location
you want your package to be published at. Make sure you uncheck the “Enable Model Versioning Box”. Click
the next Button.
24. Next window is Add Security window. You can add security
groups for your package if you wish to. The groups included here will only get
the rights to republish the package.
There are three types of security settings
a. Package Level
b .Data Level (Row level)
c .Object Level
Click the next button.
25. Next window is options window.
Make sure the check box for “Verify
Model before publishing” is checked.
Click on the Publish button.
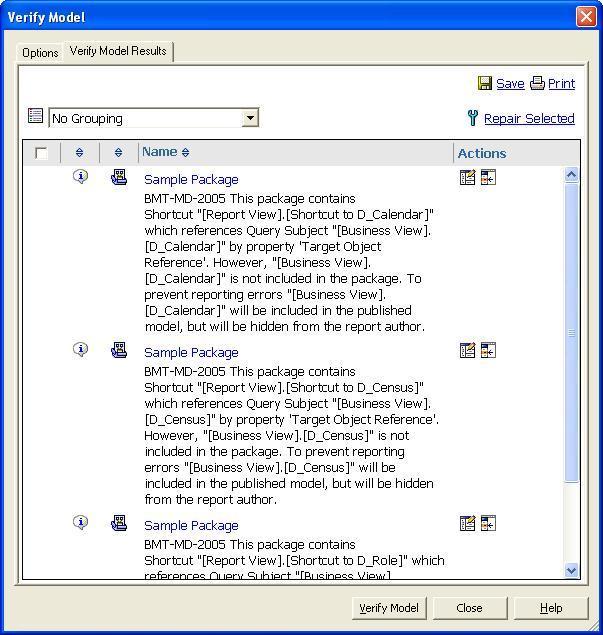
26. After you click on Publish you get following window
which provides the result of verification. Click the close button.
27. Now if you go to Cognos
Connection , you can see the published package as shown in the screen shot
below.
This is how we create a Metadata Model using Framework Manager and publish the package on cognos connection.